- Approximately 5 minutes to read
- Learning objectives:
- Understanding Placement Check in the SmartNav System
- Interpreting impedance measurements
- Utilizing Neural Response Telemetry
Intraoperative testing using tools such as Nucleus® SmartNav may provide surgeons and audiologists valuable real-time insights regarding the surgery, device function, and neural response to stimulation. The operating room (OR) is also a unique environment that requires quick decision-making and interpretation of the information available to the surgical team. This article will help provide surgeons and audiologists a better understanding of Placement Check, Impedance telemetry and Neural Response Telemetry (NRT) in the OR and interpretation of those results.
What is Placement Check?
The Placement Check algorithm is an extremely valuable new tool which helps surgeons confirm proper placement of the electrode array. To do this, Placement Check analyzes trans-impedance patterns between electrodes across the electrode array. This is performed by delivering stimulation through each electrode and recording the subsequent current level on all other intracochlear electrodes. The algorithm expects specific patterns of current flow in a normal cochlea. To ensure any potential issue with placement is identified, Placement Check is designed to be very sensitive and will automatically detect anomalies where there is a high probability of a fold or even subtle variations in expected current patterns. When a potential issue is identified, SmartNav’s Placement Check indicates the range of electrodes likely effected. In these situations, imaging may be considered to further confirm placement of the array, especially in cases of abnormal anatomy where current flow within the cochlea may also be atypical.
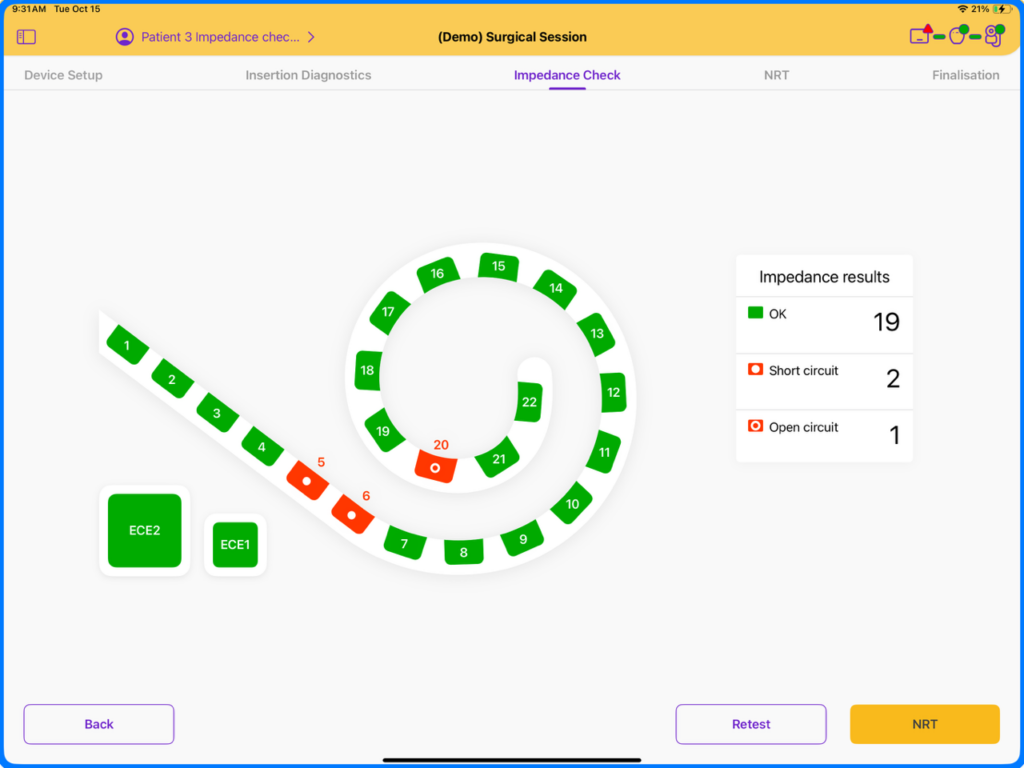
What do Impedances tell us?
The purpose of the impedance measurement is to ascertain the electrical status of individual electrodes. The impedance of an electrode not only reflects the electrical status of the electrode but also the resistance to the flow of electrical current through surrounding tissues (i.e. fluid, fibrous tissue, bone). Normal impedances will be reflected as ‘green’ in SmartNav and will have impedance values less than 30 kOhms. Normal impedance findings confirm normal electrical function of implant electrodes.
How to interpret Impedance anomalies in the OR
Incidence of electrode anomalies is rare, occurring in only 0.7% of electrodes.1 In addition to this, Goehring et al reported 82% of electrodes with abnormal intraoperative impedance resolved by the postoperative interval.² However, understanding the difference between open circuits and short circuits and potential for resolution is important in the OR.
- Open Circuits are defined as where the continuity has been broken by an interruption in the path for electrons to flow. Gushers, abnormal anatomy, or air bubbles are thought to contribute to prevalence of open circuits, making them more common intraoperatively and also more likely to resolve by postoperative fitting. 2,3
- A short circuit is when there is little or no resistance to the flow of electrons between two electrodes and occurs rarely in only 8% of cases where electrode anomalies are observed intraoperatively. 2,3
- Multiple electrode anomalies or a high ECE2 (MP2) may also affect SmartNav’s ability to obtain Placement Check. In some cases, this may be resolved through reconditioning the electrode by repeating the Impedance and Placement Check measures.
Abnormal impedance findings should be evaluated case-by-case with consideration to type of electrode anomaly (open vs short), number of electrodes affected, anatomy, potential air bubbles, or other potential contributing intraoperative factors. For support with intraoperative questions, contact our Surgical On-Call team at (877) 279-5411.
What information does Neural Response Telemetry (NRT) provide?
SmartNav has the ability to perform AutoNRT and/or Advanced NRT. The NRT measurement records the synchronous neural response, also referred to as the Evoked Compound Action Potential (ECAP) occurring in response to electrical stimulation in the cochlea. NRT is present in approximately 96% of patients, and in conjunction with other measures, can provide added confidence for postoperative counseling and activation.4
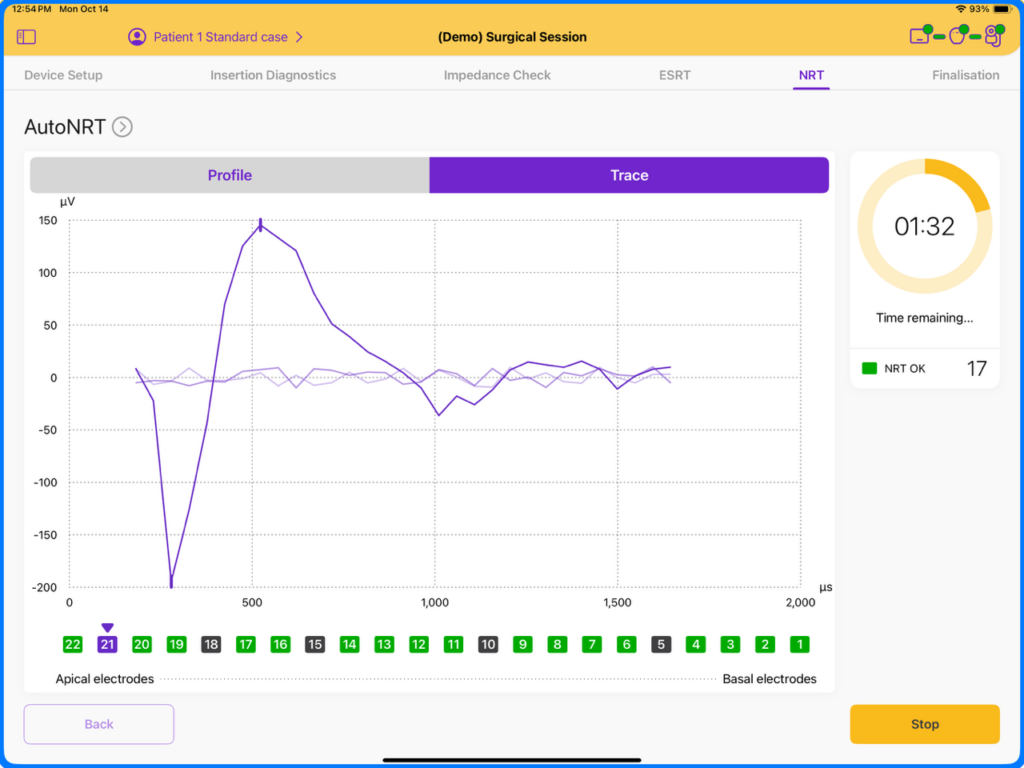
What if my patient does not have NRT responses?
NRT is a peripheral neural response and is not considered a test of hearing. Neural Response Telemetry recording parameters are also more limited compared to those which can be utilized when programming. Some patients may require different parameters in their MAP to hear with their cochlear implant. In addition to this, Absent NRT responses are not an indication of device malfunction. If NRT is unexpectedly absent, impedances and Placement Check should be confirmed, and imaging may be considered to further evaluate placement of the electrode array.
The intraoperative measurements discussed including Placement Check, Impedances and Neural Response Telemetry provide valuable information during surgery. Although tools such as SmartNav are designed with an intuitive workflow, interpretation may be required if atypical findings present. Understanding the differences between these measures, potential results, and implications will optimize the surgical experience and deliver added assurance that surgery was successful. For more information about SmartNav, please reach out to your local Cochlear Representative or visit this website: https://www.cochlear.com/us/en/professionals/connected-care/surgical-care
1. Mehta N, Chu P, Birman C.S. To Use the Back-up Cochlear Implant or Not? Using Intraoperative Impedance to Guide Your Decisions. Otol Neurotol. 2022; 43:e408-e413.
2. Goehring JL, Hughes ML, Baudhuin JL, Lusk RP. How well do cochlear implant intraoperative impedance measures predict postoperative electrode function? Otol Neurotol. 2013; 34:239–44.
3. Kuphaldt, T.R. (2006). Lessons in Electric Circuits, Volume I – DC. Fifth Edition. Retrieved from: http://www-mdp.eng.cam.ac.uk/web/library/enginfo/textbooks_dvd_only/lessons_pdf/DC.pdf
4. Cafarelli Dees D, Dillier N, Lai WK, von Wallenberg E, van Dijk B, Akdas F, Aksit M, Batman C, Beynon A, Burdo S, Chanal JM, Collet L, Conway M, Coudert C, Craddock L, Cullington H, Deggouj N, Fraysse B, Grabel S, Kiefer J, Kiss JG, Lenarz T, Mair A, Maune S, Müller-Deile J, Piron JP, Razza S, Tasche C, Thai-Van H, Toth F, Truy E, Uziel A, Smoorenburg GF. Normative findings of electrically evoked compound action potential measurements using the neural response telemetry of the Nucleus CI24M cochlear implant system. Audiol Neurootol. 2005 Mar-Apr;10(2):105-16. doi: 10.1159/000083366. Epub 2005 Jan 12. PMID: 15650302.